Hunter Platform
HUNTER PLATFORM
EMPOWER THREAT HUNTERS WITH SUPERIOR HUNTING CONTENT
HUNTER is a web-based portal that gives your threat hunters an alternative to the simplistic, stale content provided by open sources and security tool vendors.
MEET
HUNTER: THE THREAT HUNTING CONTENT PLATFORM
The HUNTER platform gives hunters access to fully customized and validated threat hunting content developed by ‘best of the best’ threat hunters. Continuously updated, fully contextualized, and easily searchable, hunters can quickly identify content that supports objectives and fills gaps in your cybersecurity program.
Reduce
Detect
Run
Remediate
LOREM IPSUM
Benefits
- Explore
- Deploy
- Hunt
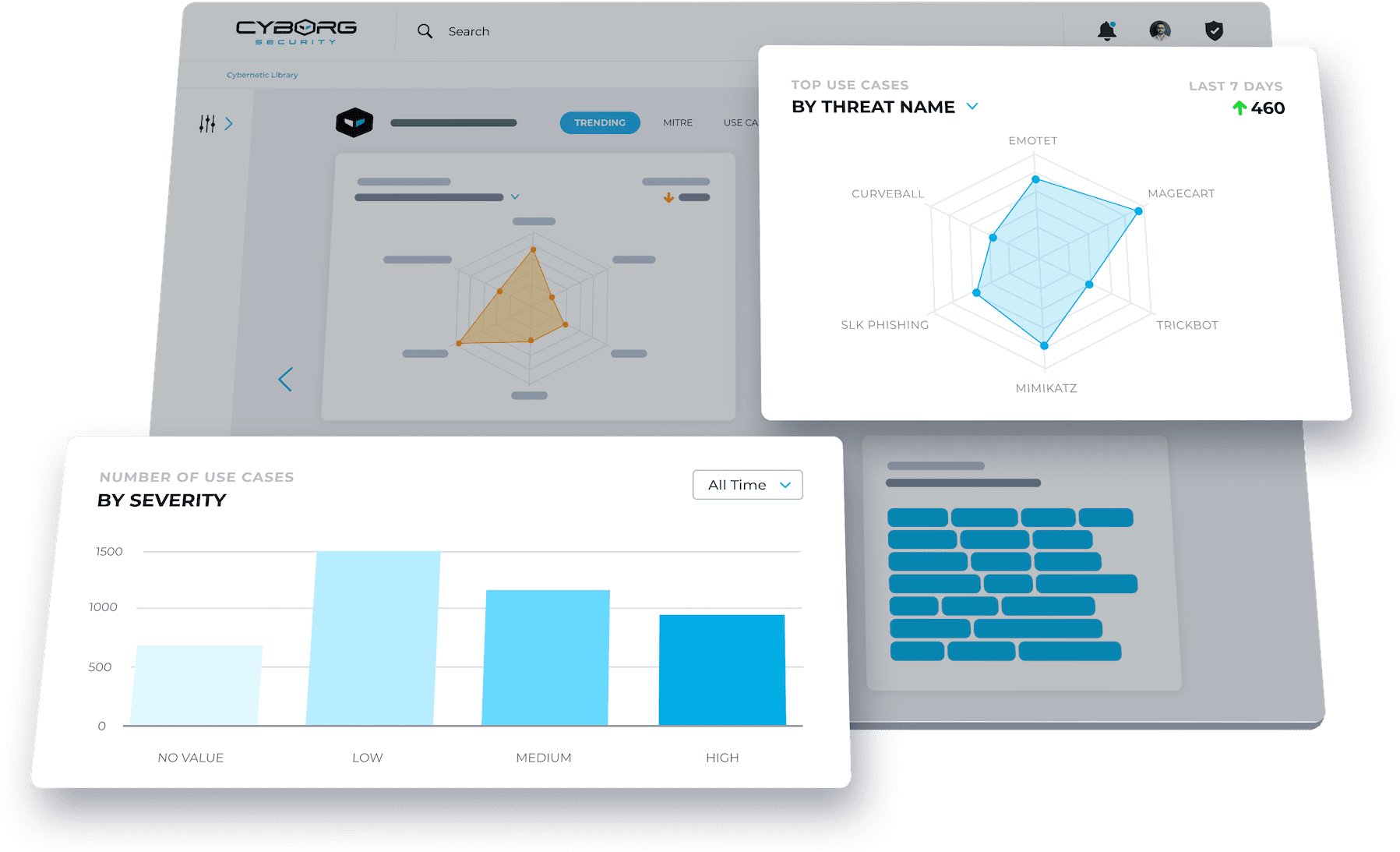
SEARCH FOR READY-MADE HUNTS
Browse or search hundreds of fully tagged and current threat hunting packages, mapped to common frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK, Cyber Kill Chain, and Diamond Model.
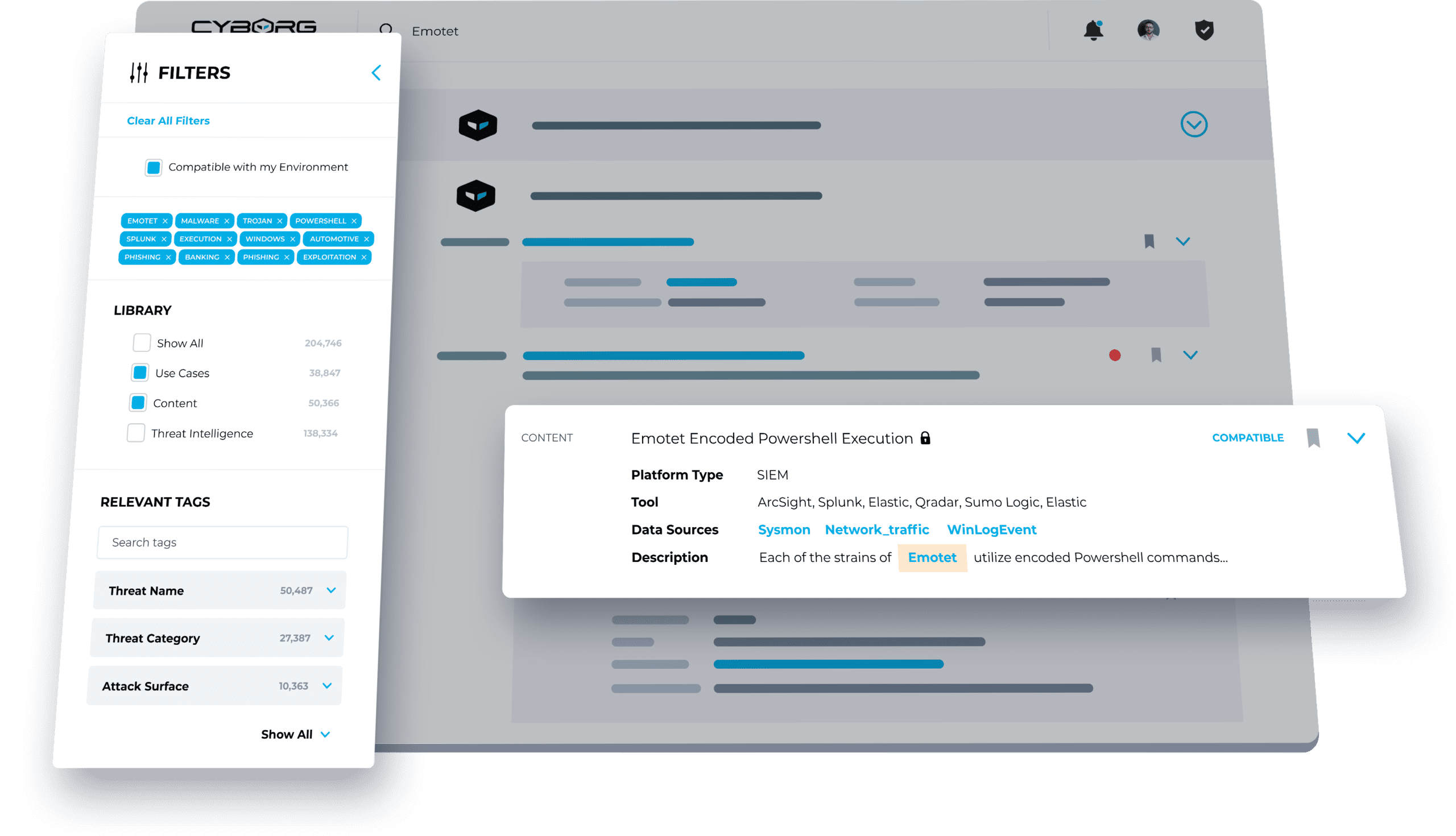
CUSTOMIZE AND DEPLOY HUNTING CONTENT
Customize threat hunting content to your SIEM, data lake, EDR, and other security tools with a single click, then deploy with confidence following clear instructions.

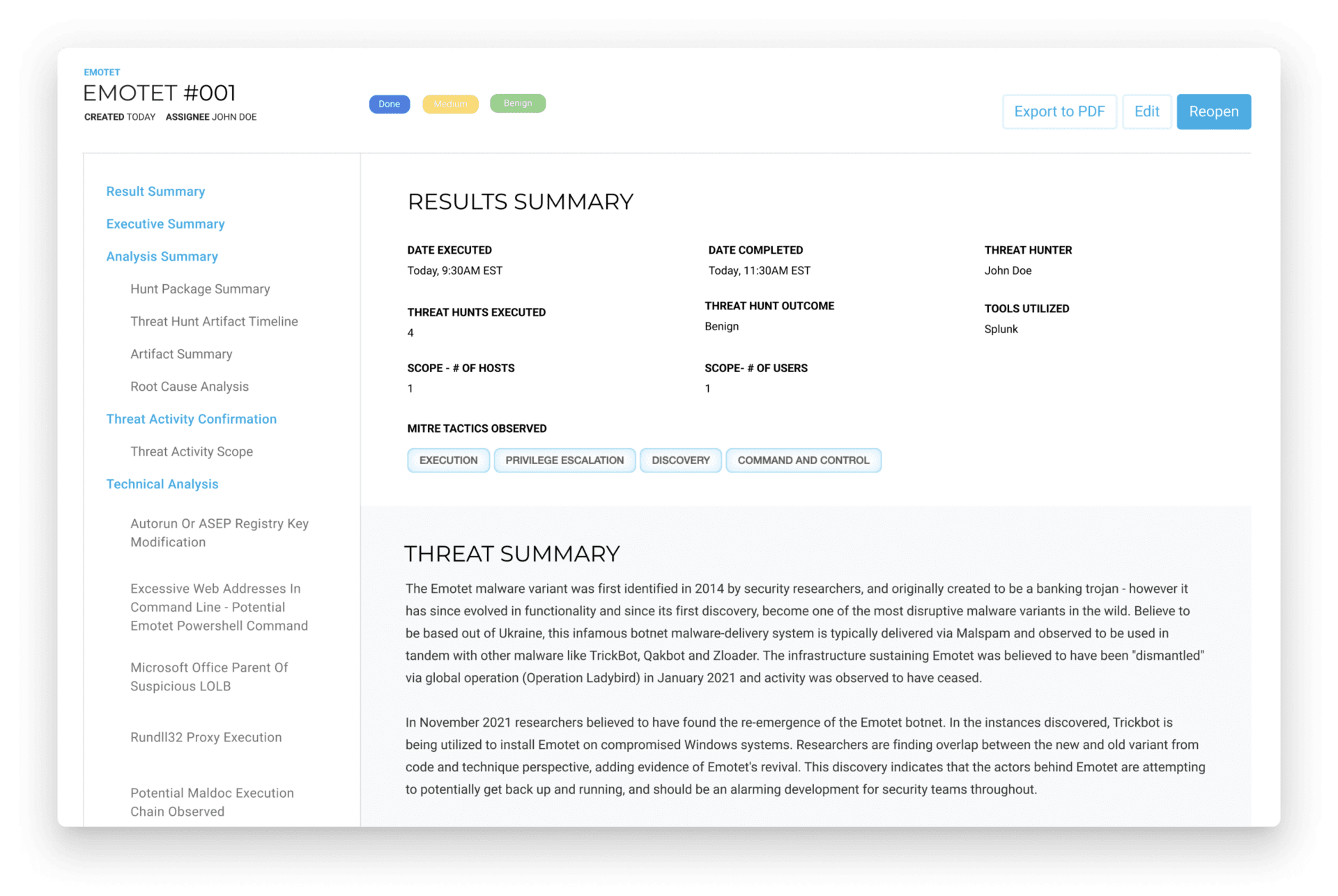
FIND AND REMEDIATE THREATS
Get full guidance to run each hunt, including how it works, what it looks for, and how IR and SOC analysts can ensure consistent, best practice remediation.

HUNT PACKAGES
- Choose from hundreds of fully contextualized hunt packages.
- Each hunt package is developed by some of the top threat hunters in the industry.
- Deploy hunts for the latest threats within hours, not weeks or months.
- All packages are current, so your team will never waste time on outdated content.
- Packages are aligned to industry frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK, Cyber Kill Chain, and Diamond Model.
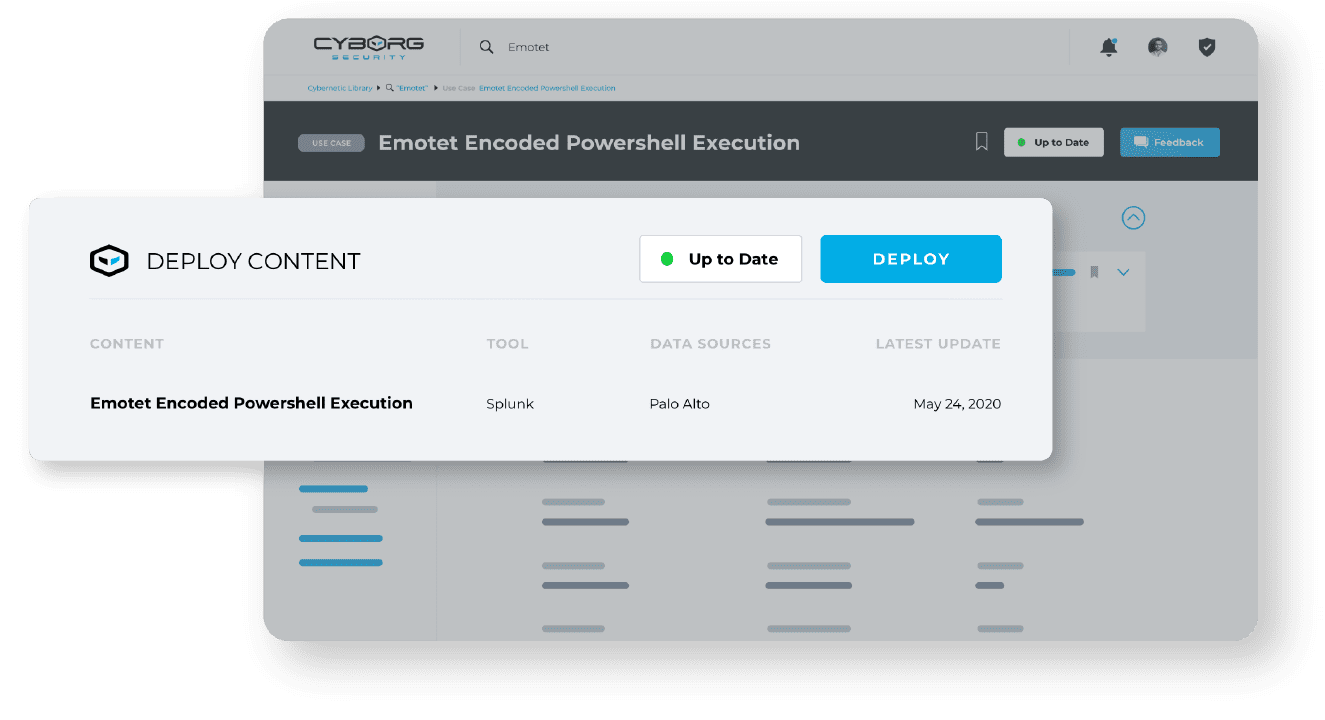
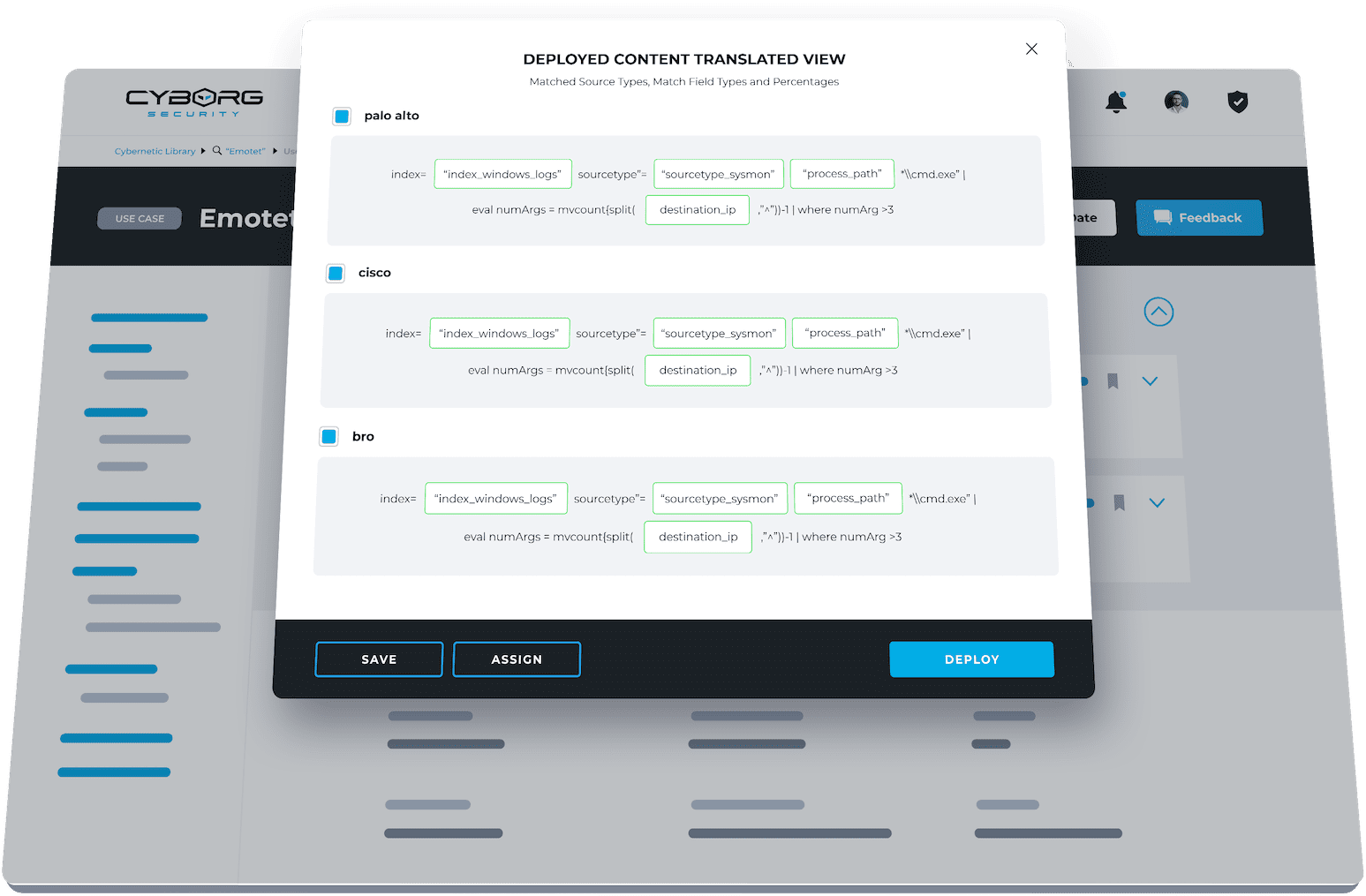
CUSTOMIZED TO YOUR ENVIRONMENT
- Effortlessly customize any package to your unique environment.
- Easily alter matched fields, indexes, and source types to ensure compatibility.
- Deploy packages out-of-the-box, with no major configuration or adjustments needed.
- Hunt outputs are tailored to your environment, so no time is wasted normalizing data.
EMULATION & VALIDATION
- Deploy advanced adversary and attack simulations
- Simulate a wide array of attack scenarios non-destructively
- Emulate adversaries to validate deployed and existing content.

SCHEDULE & MANAGE UPCOMING AND ONGOING HUNTS
- Enable collaborative hunting across security teams.
- Assign, manage, and monitor individual hunt progress.
- Provide easy management of hunt findings and remediation.
- Build customized and reusable hunt templates that can be easily scheduled.
- Provide easy-to-consume reporting including scope, timeline, evidence, and outcome.
BETTER CONTENT ENABLES MORE EFFECTIVE THREAT HUNTS
WHAT’S IN A THREAT HUNT PACKAGE?

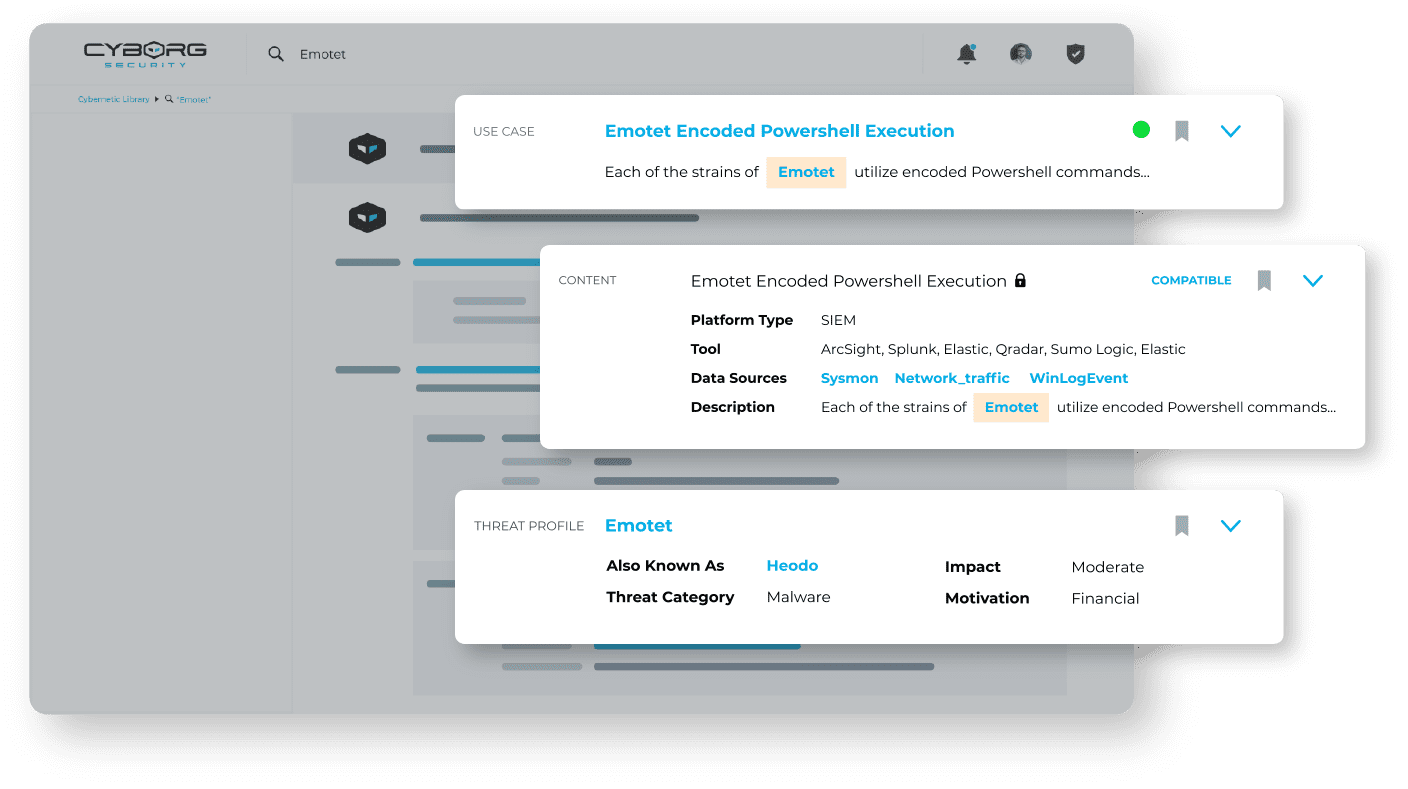
01. USE CASE & QUERY
- A clear, concise use case overview of the package, including an explanation of what it detects and how.
- An up-to-the-minute query customized for your security tools (e.g., SIEM, EDR) that goes way beyond IoC monitoring to detect specific threat actor tactics, techniques, and behaviors (TTPs).

02. CONTEXT & DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
- Analyst-focused documentation to guide the hunt and provide next steps and advice.
- Remediation guidance for analysts to ensure each threat is remediated consistently in line with best practices.

03. RUNBOOK & REMEDIATION
- A clear, concise use case overview of the package, including an explanation of what it detects and how.
- An up-to-the-minute query customized for your security tools (e.g., SIEM, EDR) that goes way beyond IoC monitoring to detect specific threat actor tactics, techniques, and behaviors (TTPs).

04. CYBER THREAT EMULATION
- Tools to emulate each threat inside your environment in a non-destructive manner.
REACTIVE TO PROACTIVE
SOLVE THREAT HUNTING CHALLENGES
COMMON CHALLENGES
- Limited time to develop hunts
- Customizing content takes too long
- Slow to address new threats
- Hard to upskill new threat hunters
- Budget constraints
THE HUNTER SOLUTION
- Reduce time to deployment by up to 95%
- Content customized to your environment
- Hunts available for new threats in 1-2 days
- Follow seasoned threat hunters processes and workflows
- Pay less than the cost of one extra FTE
MORE HUNTS, BETTER RESULTS, LESS TIME
HUNTER MAKES YOUR THREAT HUNTS:
- Fast
- Frequent
- Guided
- Consistent
DEPLOY HUNTS FASTER
Threat hunting teams often struggle to build, validate, and deploy hunts quickly. HUNTER provides a constant supply of rigorously vetted threat hunt and detection packages that your team can deploy up to 95% faster than hunts developed in-house.
- Run customized hunts out-of-the-box with minimal (if any) changes.
- Quickly validate content and emulate threats with ready-made tools and guidance.
- Deploy hunts for brand new threats in days, not weeks.
RUN MORE HUNTS
Most hunting teams run a few hunts per month because they take time to build and validate. HUNTER provides a library of ready-to-go packages that your team can validate and deploy in a fraction of the time. That means more hunts with less effort—and no additional FTEs.
- Increase hunt output by 5X (or even more).
- Dramatically improve the mean time to deployment (MTTDp).
- Increase the number and speed of hunts without sacrificing quality.
GUIDE YOUR THREAT HUNTING
A common challenge for threat hunters is knowing which hunts to develop first. HUNTER packages are based on current TTPs, high-fidelity CTI, and adversary behaviors, allowing threat hunters to select hunts based on the threats currently focused on your industry or location.
- Reduce cyber risk by focusing hunts on the most pressing threats.
- Avoid wasting time on hunts that aren’t likely to yield results.
- New threat hunters can analyze expert-developed packages to guide future hunts.
REMEDIATE THREATS CONSISTENTLY
Remediation is a crucial part of threat hunting but isn’t always approached consistently. Often, analysts simply reimage infected assets, running the risk that a threat has spread to other assets. HUNTER packages include best practice guidance to fully remediate every threat.
- Guide incident responders to ensure effective, consistent remediation.
- Uncover the full extent of threats, rather than focusing exclusively on one asset.
- Dramatically reduce cyber risk posed by unidentified threats.
COMPATIBILITY
SEAMLESS INTEGRATION
The HUNTER Platform integrates seamlessly with a wide variety of security and data management tools.










Episode 16
JOIN US FOR AN EVENING OF THREAT HUNTING FUN! Cyborg Security has launched a podcast with a twist! Join us for the first fully interactive

SANS 2024 Threat Hunting Survey: Hunting for Normal Within Chaos
Discover the Cutting-Edge of Cybersecurity in the “SANS 2024 Threat Hunting Survey: Hunting for Normal Within Chaos” Are you navigating the complexities of threat hunting

Threat-Informed Defense through Behavioral Threat Hunting
In the cybersecurity domain, the evolution from a purely reactive stance to a proactive, anticipatory approach encapsulates the transition to a Threat-Informed Defense strategy. This
